Shaft mining is a method of extracting valuable minerals and ores from deep underground deposits. This technique involves the construction of vertical shafts that allow miners to access mineral resources located beneath the Earth’s surface. Shaft mining is particularly effective for minerals found in hard rock formations, such as gold, silver, copper, and zinc. This article explores the techniques used in shaft mining, its advantages, challenges, and its significance in the mining industry.
What is Shaft Mining?
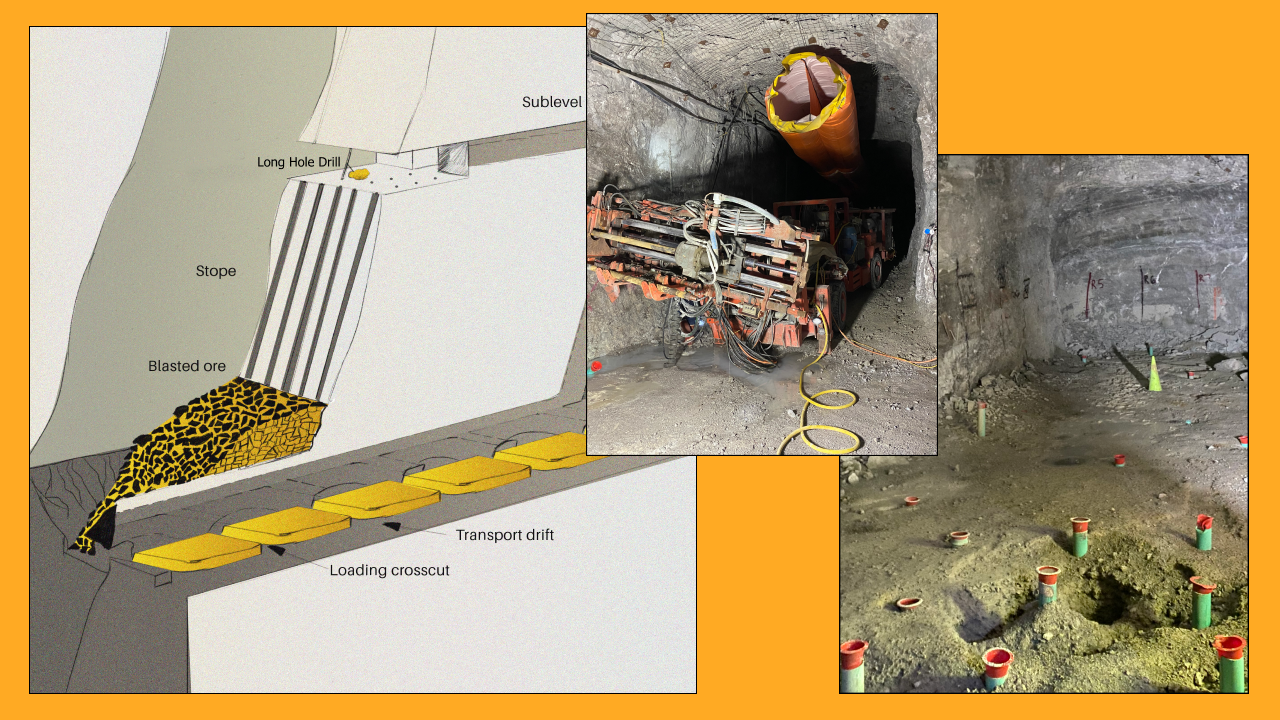
Shaft mining is a form of underground mining that requires the excavation of vertical shafts to reach ore deposits located deep beneath the surface. This method is particularly useful for extracting minerals that are too deep for surface mining techniques. Once a shaft is established, horizontal tunnels, known as drifts, are created to access the ore bodies.
Techniques Used in Shaft Mining
- Site Preparation: Before shaft construction begins, a detailed geological survey is conducted to identify the location and extent of the ore deposit. Environmental assessments are also performed to minimize ecological impact.
- Shaft Construction: The shaft is excavated vertically, often using drilling and blasting techniques to break up rock. This process can take several months and involves the removal of significant amounts of overburden.
- Access and Support Systems: As the shaft is excavated, support structures are installed to ensure the safety and stability of the walls. This may include concrete linings or steel supports.
- Hoisting Systems: Once the shaft is established, hoisting systems are installed to transport ore, waste material, and personnel to and from the surface. This typically involves the use of cages or skips that move up and down the shaft.
- Drifting: Horizontal tunnels are created from the shaft to access the ore body. Miners extract the ore using various techniques, including drilling, blasting, and mucking (removing broken rock).
- Ventilation: Effective ventilation systems are critical in shaft mining to ensure air quality and temperature control. Fresh air is pumped into the mine while stale air is expelled to maintain safe working conditions.
Advantages of Shaft Mining
- Access to Deep Deposits: Shaft mining allows miners to reach valuable resources located deep underground, making it a preferred method for many mineral deposits that cannot be accessed by surface mining.
- Minimal Surface Disruption: Compared to surface mining techniques, shaft mining has a lower impact on the landscape, preserving the surface environment and ecosystems.
- Higher Recovery Rates: The controlled environment of underground mining can lead to higher recovery rates of ore, particularly in complex deposits where surface mining might miss significant amounts.
- Safety: When properly managed, shaft mining can be safer than some surface mining methods, as the risks associated with landslides and rockfalls are minimized.
Challenges of Shaft Mining
- High Costs: The initial investment for shaft construction and the associated infrastructure can be substantial. This includes the costs of drilling, blasting, and installing hoisting and ventilation systems.
- Safety Risks: Despite being generally safer than some surface methods, shaft mining still poses risks, including cave-ins, flooding, and exposure to harmful gases.
- Ventilation and Water Management: Maintaining proper ventilation is essential for worker safety, and managing groundwater can be challenging and costly, especially in regions with high water tables.
- Regulatory and Environmental Concerns: Shaft mining operations must comply with strict regulations regarding land use, water quality, and worker safety, which can complicate project planning and execution.
The Role of Shaft Mining in the Industry
Shaft mining plays a crucial role in the mining industry, particularly for the extraction of high-value minerals found in hard rock formations. Countries with rich mineral deposits, such as Canada, Australia, and South Africa, often employ shaft mining to access deep ore bodies.
The method is particularly significant for minerals like gold and platinum, where deep deposits require advanced mining techniques. As the demand for these resources continues, the efficiency and safety of shaft mining will be essential in meeting global needs.
Innovations in Shaft Mining
The future of shaft mining is being shaped by advancements in technology aimed at enhancing safety and efficiency. Key innovations include:
- Automation: The integration of automated systems and robotics can improve safety and productivity by reducing the need for human intervention in hazardous areas.
- Data Analytics: Advanced data analysis helps optimize mining operations, improve decision-making, and enhance resource recovery.
- Sustainable Practices: Many mining companies are adopting more sustainable practices, such as reducing water usage, minimizing waste, and restoring habitats post-mining.
Conclusion
Shaft mining is a vital technique for extracting valuable minerals from deep underground deposits. While it offers numerous advantages, including access to rich ore bodies and minimal surface disruption, it also presents challenges related to safety, cost, and environmental impact. As the mining industry continues to evolve, innovations in technology and sustainable practices will play a crucial role in shaping the future of shaft mining, ensuring it remains a key method for meeting global mineral demands while prioritizing safety and environmental stewardship.

![Discovering the Hidden Gems of [Region Name]](https://bromine.info/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/Tips-to-attract-domestic-and-regional-markets-Study-Banner.jpg)
