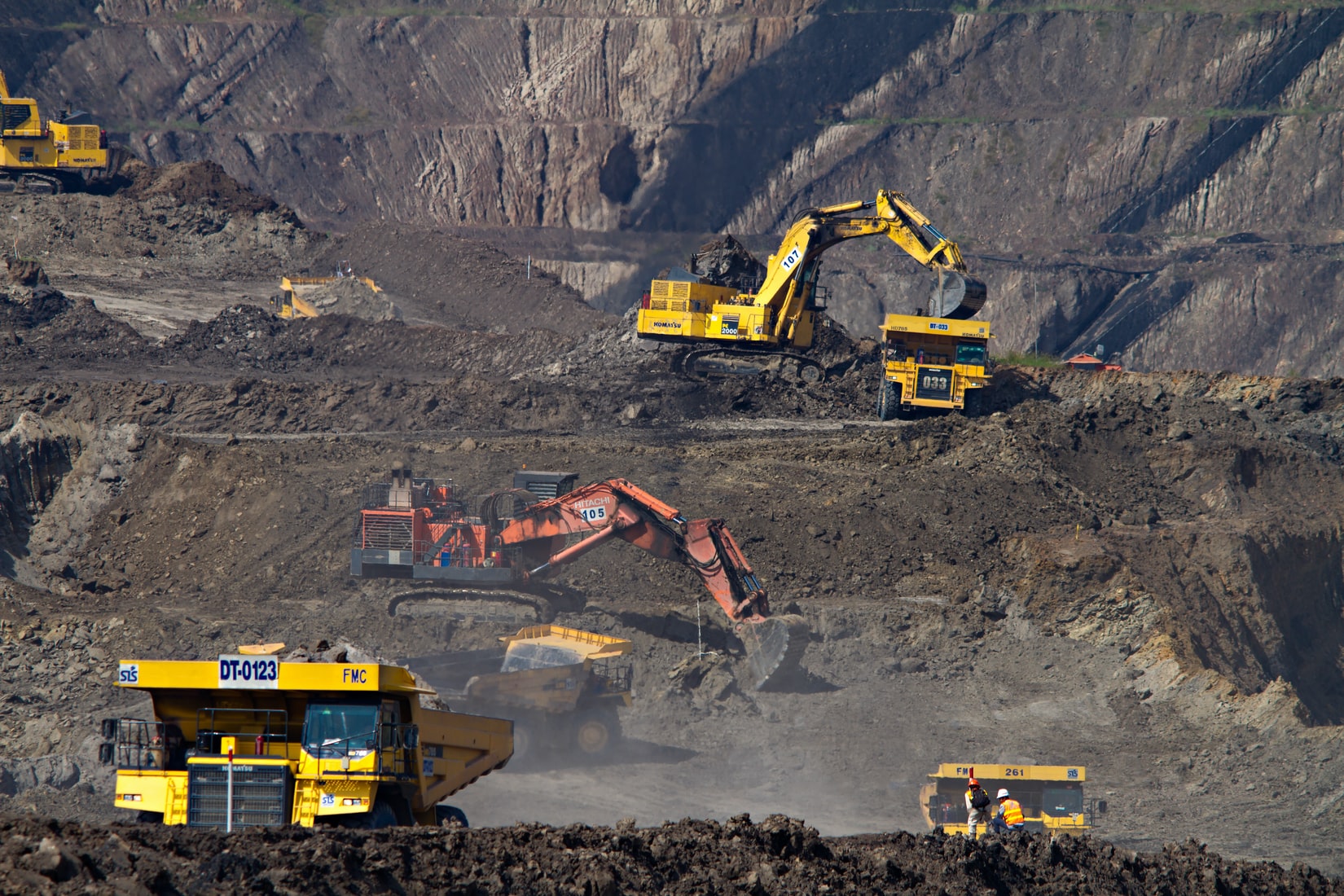
Quarrying, the process of extracting stone and aggregates from the earth, has been a fundamental practice since ancient times, providing essential materials for construction, infrastructure, and various industrial applications. This article delves into the methods of quarrying, its environmental and social impacts, and the innovative approaches being adopted to enhance sustainability in the industry.
Understanding Quarrying
Quarrying primarily involves the extraction of hard materials such as granite, limestone, sandstone, and marble. These materials are used in various applications, including:
- Construction: Aggregates from quarries are essential for concrete, asphalt, and road base.
- Dimension Stone: Natural stones, cut into specific sizes for architectural and decorative purposes.
- Industrial Applications: Materials like limestone are used in manufacturing cement and glass.
Methods of Quarrying
The methods employed in quarrying can vary significantly based on the type of material being extracted and the specific geology of the site. The most common techniques include:
- Open-Pit Quarrying: This method involves the removal of large sections of earth to expose the stone or aggregate. It is commonly used for materials like granite and limestone.
- Drilling and Blasting: For hard rock quarries, controlled blasting is often necessary to fracture the rock before it can be extracted. This technique is carefully managed to minimize environmental impact.
- Wire Sawing: This method employs a wire with diamond-tipped segments to cut through stone with precision, reducing waste and allowing for better control over the final product.
- Hydraulic Excavation: Used in softer materials, this technique involves using hydraulic machinery to scoop out the material without the need for blasting.
Environmental and Social Impacts
While quarrying provides critical resources, it also poses several environmental and social challenges:
- Ecosystem Disruption: Quarrying can lead to habitat destruction, affecting local flora and fauna. The removal of vegetation can result in soil erosion and disruption of local ecosystems.
- Water Management Issues: Quarrying activities can alter local water tables and drainage patterns, leading to potential water shortages or contamination of groundwater sources.
- Dust and Air Quality: Dust generated from quarry operations can affect air quality, posing health risks to workers and nearby communities.
- Noise Pollution: The machinery used in quarrying can produce significant noise, impacting local wildlife and residential areas.
- Community Displacement: In some cases, quarrying operations may lead to the displacement of local communities, raising ethical concerns regarding land use and rights.
Innovations and Sustainable Practices
In response to the challenges associated with quarrying, the industry is increasingly adopting sustainable practices and innovative technologies. Some key developments include:
- Reclamation and Restoration: Many quarries are now required to implement reclamation plans to restore land post-extraction. This may involve re-vegetation, habitat creation, and other measures to rehabilitate the landscape.
- Water Management Technologies: Implementing systems to manage and recycle water used in quarrying processes helps minimize environmental impact and preserve local water resources.
- Dust Control Measures: Techniques such as water spraying and dust suppression agents are being employed to reduce airborne dust and improve air quality.
- Sustainable Quarrying Certifications: Various organizations are establishing certifications for sustainable quarrying practices, encouraging companies to adhere to environmental and social standards.
- Use of Technology: Advances in technology, such as drones for site surveying and monitoring, are improving efficiency and reducing environmental impacts in quarry operations.
Conclusion
Quarrying is an essential industry that provides vital materials for construction and infrastructure development. However, it is not without its challenges, particularly concerning environmental and social impacts. By adopting innovative practices and prioritizing sustainability, the quarrying industry can mitigate these impacts while continuing to meet the demands of a growing population and economy. As stakeholders increasingly recognize the importance of responsible resource extraction, the future of quarrying holds promise for a more sustainable approach that benefits both industry and communities alike.