Open-pit mining, also known as open-cast or open-cut mining, is a widely used method for extracting minerals and resources from the Earth’s surface. This approach is particularly effective for minerals located near the surface, such as copper, gold, iron, and coal. While open-pit mining can yield substantial economic benefits, it also poses significant environmental challenges. This article delves into the techniques used in open-pit mining, its advantages and disadvantages, and its role in the global mining industry.
What is Open-Pit Mining?
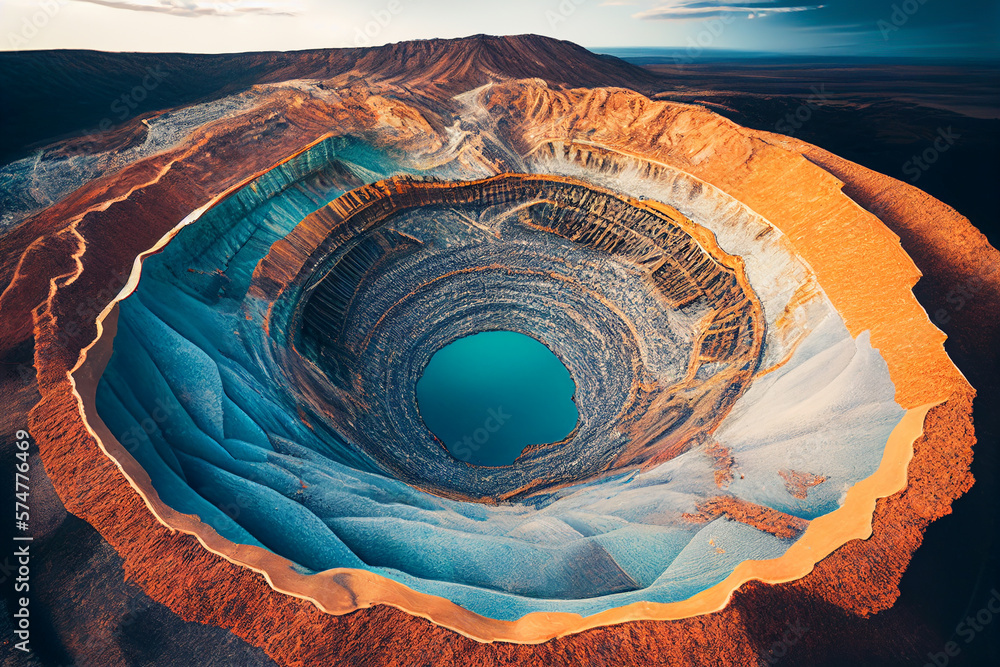
Open-pit mining involves the removal of overburden (soil and rock layers) to access mineral deposits. The process begins with the excavation of a large, open pit, which is gradually expanded as mining progresses. The design of the pit typically resembles a series of terraces or benches, allowing for the safe extraction of materials and the transportation of equipment.
Techniques of Open-Pit Mining
- Site Preparation: Before mining begins, the site is cleared of vegetation and surface materials. This preparation involves extensive surveying and planning to determine the best method of extraction.
- Drilling and Blasting: Holes are drilled into the rock, which are then filled with explosives. Controlled blasting breaks up the rock, allowing for easier excavation.
- Excavation: After blasting, heavy machinery such as excavators and shovels are used to remove the broken rock. The material is transported to processing facilities for further separation of valuable minerals.
- Hauling: Dump trucks are used to haul the mined material to processing plants or waste dumps. The transportation of materials is a critical component of the mining process.
- Reclamation: After mining operations cease, the site undergoes reclamation to restore the landscape. This may involve backfilling the pit, reshaping the land, and reintroducing vegetation to stabilize the soil.
Advantages of Open-Pit Mining
- Cost-Effective: Open-pit mining is often more cost-effective than underground mining. The removal of overburden is less expensive, and the larger scale of operations allows for economies of scale.
- High Production Rates: This method enables the extraction of large volumes of material quickly, making it ideal for large deposits of minerals.
- Safety: Open-pit mining generally poses fewer safety risks to workers compared to underground mining. The risks associated with cave-ins and confined spaces are minimized.
- Accessibility: The design of open pits allows for easier access to the extracted materials, enabling efficient transportation and processing.
Disadvantages of Open-Pit Mining
- Environmental Impact: Open-pit mining can lead to significant environmental degradation. The removal of vegetation, alteration of landscapes, and potential contamination of soil and water bodies are major concerns.
- Habitat Destruction: The extensive land disturbance can destroy habitats for local wildlife, leading to biodiversity loss.
- Visual Impact: The large, open pits are often visually intrusive, affecting the aesthetics of the surrounding landscape.
- Waste Generation: Open-pit mining generates a substantial amount of waste material, which must be managed to prevent environmental contamination.
The Role of Open-Pit Mining in the Industry
Open-pit mining plays a vital role in the global mining industry, particularly for the extraction of certain minerals. It is a preferred method for mining large, low-grade deposits where the mineral is distributed over a broad area. Countries rich in resources such as Australia, Canada, and the United States utilize open-pit mining extensively to meet the demand for metals and minerals.
Mitigating Environmental Impacts
Recognizing the environmental challenges associated with open-pit mining, many companies are adopting more sustainable practices. This includes:
- Reclamation Planning: Implementing comprehensive reclamation plans before mining begins to ensure that land is restored post-extraction.
- Erosion Control: Utilizing techniques to control soil erosion and manage water runoff to prevent contamination.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Establishing programs to protect local flora and fauna during and after mining operations.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in decision-making processes and addressing their concerns about environmental and social impacts.
Conclusion
Open-pit mining is a crucial method for extracting valuable resources that support modern society. While it offers significant economic benefits and operational efficiencies, it also presents environmental challenges that must be managed carefully. As the mining industry evolves, there is a growing emphasis on sustainable practices that minimize the ecological footprint of open-pit mining. By balancing resource extraction with environmental stewardship, the industry can work toward a more sustainable future that meets both economic needs and environmental responsibilities.