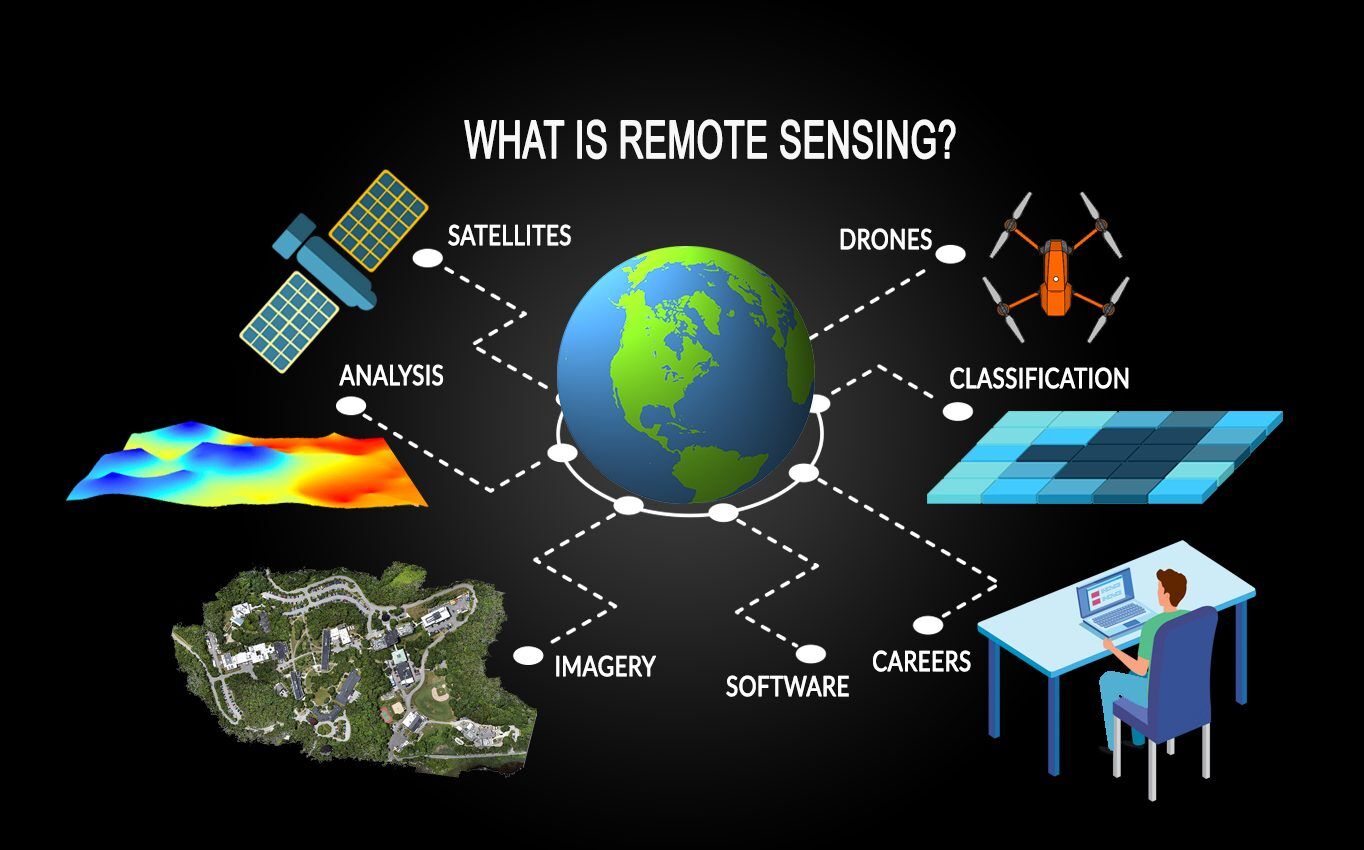
Remote sensing is a powerful technology that allows for the collection and analysis of data about the Earth’s surface from a distance, typically using satellite or aerial imagery. In the mining industry, remote sensing plays a crucial role in exploration, monitoring, and management, providing valuable insights that enhance operational efficiency and sustainability. This article delves into the applications, benefits, challenges, and future prospects of remote sensing in mining.
Applications of Remote Sensing in Mining
- Mineral Exploration:
- Remote sensing is extensively used in the early stages of mineral exploration. Satellite images and aerial surveys can identify geological features and mineral deposits, helping geologists pinpoint areas for further investigation.
- Geological Mapping:
- High-resolution imagery enables detailed geological mapping, revealing rock types, structures, and alterations in the landscape. This information is vital for understanding mineral distribution and informing extraction strategies.
- Environmental Monitoring:
- Remote sensing technologies help monitor environmental changes resulting from mining activities. They can assess land degradation, deforestation, water quality, and the health of surrounding ecosystems, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
- Land Use Planning:
- Remote sensing aids in effective land use planning by providing insights into land cover and land use changes. This helps mining companies understand how their operations impact local communities and environments.
- Tailings Management:
- Monitoring tailings storage facilities is crucial for preventing environmental disasters. Remote sensing can detect changes in tailings dam conditions, providing early warnings of potential failures.
- Site Rehabilitation:
- After mining activities have ceased, remote sensing is used to assess the effectiveness of land reclamation efforts. It helps evaluate vegetation recovery and ecosystem restoration over time.
Benefits of Remote Sensing in Mining
- Cost-Effectiveness:
- Remote sensing reduces the need for extensive ground surveys, which can be time-consuming and expensive. This technology allows for large areas to be monitored quickly and efficiently.
- Enhanced Data Collection:
- Remote sensing provides high-quality, high-resolution data that can be collected regularly, offering a comprehensive view of mining operations and their impacts.
- Timely Decision-Making:
- The real-time data provided by remote sensing technologies allows mining companies to make informed decisions swiftly, optimizing operations and addressing issues as they arise.
- Improved Safety:
- By enabling remote monitoring of hazardous areas, remote sensing enhances worker safety. It reduces the need for personnel to enter potentially dangerous environments for inspections.
- Sustainability:
- Remote sensing supports sustainable mining practices by helping companies monitor their environmental footprint and implement measures to minimize impacts on local ecosystems.
Challenges of Remote Sensing in Mining
- Data Interpretation:
- While remote sensing provides vast amounts of data, interpreting this data accurately requires expertise in geology and remote sensing techniques. Companies may need to invest in training or hire specialists.
- Cost of Technology:
- Advanced remote sensing technologies, such as LiDAR and multispectral imaging, can be expensive. Mining companies must weigh the benefits against the costs of acquiring and implementing these technologies.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Mining operations are subject to various regulations that govern environmental monitoring and data reporting. Ensuring compliance with these regulations can be complex and time-consuming.
- Limitations of Resolution:
- The effectiveness of remote sensing can be limited by factors such as atmospheric conditions, resolution of imagery, and the presence of vegetation or other obstructions that can obscure the surface.
- Integration with Other Data:
- For remote sensing data to be most effective, it often needs to be integrated with other data sources, such as geological surveys or environmental assessments. This requires robust data management systems.
Future Prospects
The future of remote sensing in mining looks promising, with advancements in technology and methodologies. Emerging trends include:
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning:
- Combining remote sensing with AI can enhance data analysis and interpretation, allowing for more accurate predictions and assessments in mining operations.
- Improved Sensor Technology:
- Advances in sensor technology, such as hyperspectral imaging, will provide even more detailed information about mineral composition and environmental conditions.
- Increased Use of Drones:
- Drones equipped with remote sensing technologies are becoming more common in mining. They offer flexibility and high-resolution data collection, especially in hard-to-reach areas.
- Real-Time Monitoring:
- The development of satellite constellations for real-time monitoring will enable continuous observation of mining sites, improving response times to environmental changes and operational issues.
Conclusion
Remote sensing is revolutionizing the mining industry by providing essential data for exploration, monitoring, and management. Its ability to enhance efficiency, improve safety, and support sustainable practices makes it a vital tool for modern mining operations. As technology continues to advance, the integration of remote sensing into mining will likely grow, enabling companies to operate more responsibly and effectively in an increasingly resource-conscious world. By embracing these innovations, the mining industry can enhance its operational capabilities while minimizing its environmental impact.